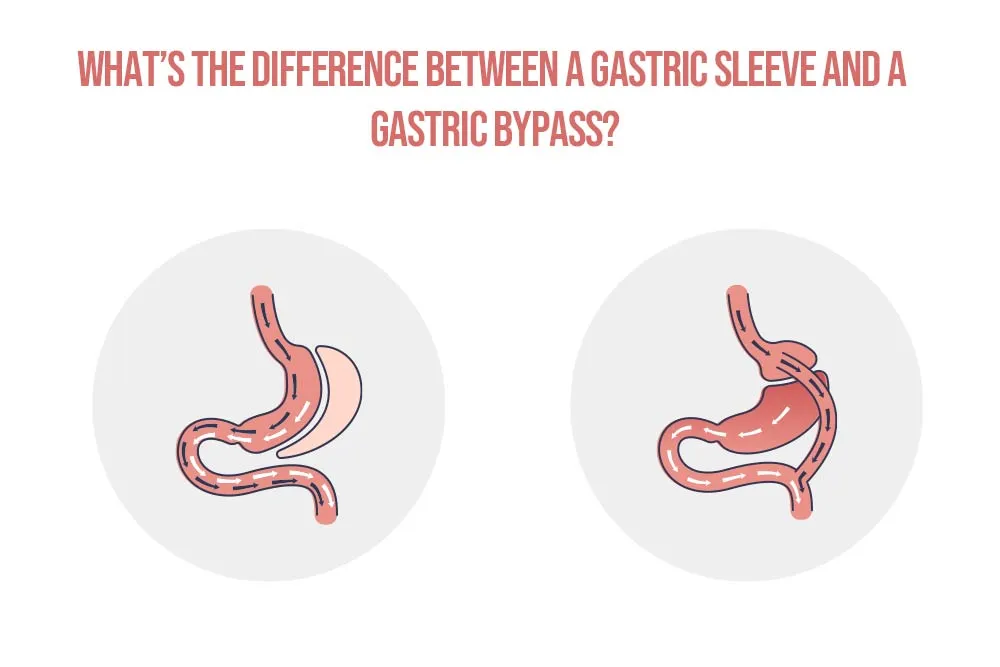
If you’re considering weight loss surgery in Ireland, you’ve likely discovered that the two procedures that stand out are the gastric sleeve and the gastric bypass. But understanding the real-world difference between them, beyond the medical diagrams, is crucial to making the right choice for your body and your future.
Think of it this way, both are powerful tools for weight loss transformation, but they work in fundamentally different ways. One is like resizing a container, while the other is like rerouting a pathway. This isn’t just a medical decision, it’s a personal one that affects your long-term health, your relationship with food, and your daily life.
This guide cuts through the confusion to give you a clear, honest, and detailed comparison of gastric sleeve versus gastric bypass procedures so you can move forward with confidence.
Comparing Gastric Sleeve vs Gastric Bypass
To help you see the difference between gastric sleeve and bypass at a glance, we’ve broken down the key elements of each procedure.
What is Gastric Sleeve Surgery and How Is It Done?
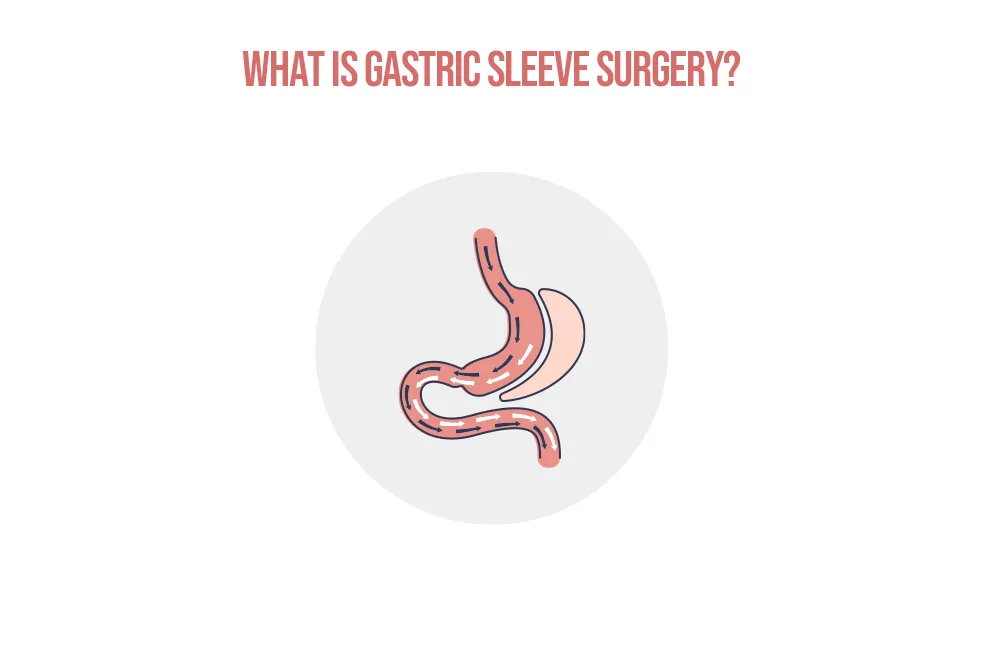
Gastric Sleeve surgery, medically known as sleeve gastrectomy, is a restrictive weight loss procedure. It focuses on permanently reducing the size of your stomach to limit how much food you can eat and to significantly reduce feelings of hunger.
The procedure is performed laparoscopically (using minimally invasive keyhole surgery). During the operation, approximately 80% of the stomach is surgically removed. This includes the fundus, the part of the stomach that produces the “hunger hormone,” ghrelin.
What remains is a narrow, tube-like, or banana-shaped “sleeve.” This new, smaller stomach holds far less food, and because the intestines are not touched or rerouted, digestion continues normally.
What is Gastric Bypass Surgery and How Is It Done?
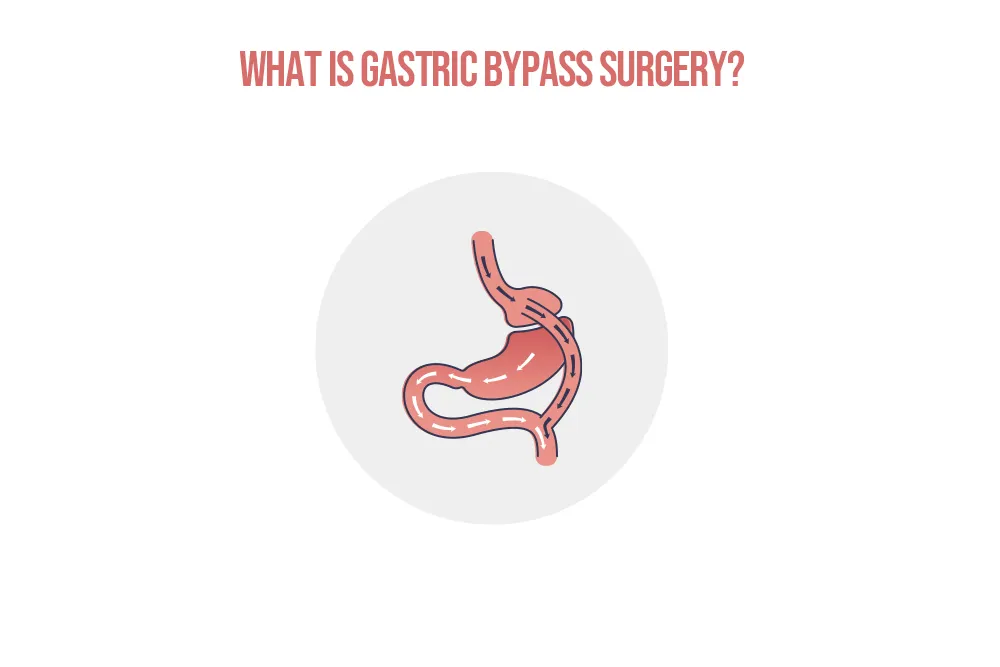
Gastric Bypass surgery, known as Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, is a more complex procedure that combines both restriction and malabsorption. It not only creates a small stomach pouch to limit food intake but also reroutes the digestive system to reduce calorie absorption.
This surgery is also performed laparoscopically and involves two key steps. First, a very small, egg-sized stomach pouch (about 30ml) is created by stapling and separating the top of the stomach from the rest. This drastically reduces food capacity.
Second, a section of the small intestine is cut and connected directly to this new pouch. This surgically created pathway “bypasses” the larger, remaining part of the stomach and the first portion of the small intestine (the duodenum), meaning food enters the lower intestine much sooner, reducing the calories and nutrients your body can absorb.
What Are the Key Benefits Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass
Gastric Sleeve Benefits:
- Strong reduction in the hunger hormone (ghrelin).
- Simpler procedure with no intestinal rerouting.
- Lower risk of long-term vitamin deficiencies compared to bypass.
- No risk of “dumping syndrome.”
- Effective improvement in obesity-related conditions like high blood pressure and sleep apnea.
Gastric Bypass Benefits:
- Dual-action: restricts food intake and reduces calorie absorption.
- Often leads to very rapid improvement or remission of Type 2 Diabetes.
- Typically results in slightly greater excess weight loss long-term.
- Can be more effective for patients with severe acid reflux (GERD).
Potential Risks and Considerations of Gastric Sleeve and Bypass
Gastric Sleeve Risks include:
- The procedure is irreversible.
- Potential for staple line leaks or bleeding.
- New or worsening acid reflux can occur in some patients.
- As with any major surgery, risks of infection or blood clots exist.
Gastric Bypass Risks include :
- Higher risk of long-term vitamin and mineral deficiencies (requires strict, lifelong supplementation).
- “Dumping syndrome” can occur if high-sugar foods are consumed.
- Risk of bowel obstruction or ulcers.
- More complex procedure, which can mean a slightly longer operating time.
Comparing Recovery Between Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass
Navigating the recovery process is a key part of your journey. While both procedures require a commitment to healing and new lifestyle habits, the timeline and experience can differ. Here’s a direct comparison of what you can generally expect.
| Recovery Aspect | Gastric Sleeve | Gastric Bypass |
| Hospital Stay | Typically 1–2 nights | Typically 2–3 nights |
| Return to Work | Most patients within 2–3 weeks | Most patients within 3–4 weeks |
| Initial Pain/Discomfort | Manageable, often around the port sites and stomach. | Can be similar, but may include more internal sensation from the intestinal re-routing. |
| Dietary Progression | Gradual progression from liquids to purees to soft foods. Must be followed carefully. | Same gradual progression, but requires extreme diligence to avoid complications like dumping syndrome. |
| Physical Activity | Light walking is encouraged immediately. Strenuous exercise and heavy lifting are restricted for 4–6 weeks. | Similar timeline, but patients may feel the need to be more cautious for a longer period due to the complexity of the procedure. |
| Long-Term Follow-up | Lifestyle commitment with annual check-ups and monitoring for nutritional levels. | Lifelong commitment with strict, mandatory vitamin/mineral supplementation and regular blood tests to prevent deficiencies. |
| Key Consideration | The focus is on healing the stomach staple line and adapting to a smaller stomach volume. | The focus is on healing both the new stomach pouch and the intestinal connection, while adapting to malabsorption. |
Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass Weight Loss Results and Timeline
When you’re investing in this journey, you naturally want to know: “How much weight will I lose, and how long will it take?” and It’s important to have realistic expectations.
With the gastric sleeve, you can typically expect to lose a remarkable 60-70% of your excess body weight. This isn’t an overnight change, it’s a steady, consistent journey. Your most rapid loss will usually happen in that first, motivating 6 to 12 months, with your weight gradually stabilising about 18 to 24 months after your surgery.
The gastric bypass often leads to a slightly higher overall loss, with patients losing an average of 70-80% of their excess body weight. Many people notice that the initial weight loss in the first 6 months can be a bit faster than with the sleeve. Your weight will settle into its new normal around the 18 to 24-month mark.
It’s crucial to remember that these numbers are a guide, not a guarantee. Your own results will be shaped by your commitment to the new dietary guidelines, incorporating physical activity, and attending your follow-up appointments.
Comparing Cost and Insurance in Ireland
Let’s talk about the practical side. Weight loss surgery is an investment in your long-term health, and it’s important to understand the financial commitment involved.
Procedure Costs:
The cost for gastric sleeve surgery in Ireland typically starts from €10,000, while gastric bypass surgery typically starts from €12,000. These figures are indicative, and a final price is always confirmed after your personal consultation, which tailors the plan to your specific needs.
Health Insurance in Ireland:
This is a common area of confusion. Gastric Sleeve is almost always considered a cosmetic or elective procedure by Irish health insurers and is generally not covered.
However, with gastric Bypass, there is a possibility for partial coverage. Some Irish insurance providers may cover a portion of the cost if the procedure is deemed medically necessary. This usually requires a detailed report from your consultant and GP.
The good news is that here at Auralia we provide you with the option to pay for the surgery in multiple monthly installments up to 36 months via our trusted financial partners.
Who Is the Ideal Candidate for Both Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass
The Gastric Sleeve is often recommended for:
- Individuals with a lower BMI (e.g., 35-45).
- Those who want to avoid the malabsorptive element of bypass.
- People without severe, uncontrolled acid reflux.
- Those committed to lifestyle changes but concerned about the complexity of bypass.
The Gastric Bypass is often recommended for:
- Individuals with a higher BMI (e.g., 45+).
- Patients with severe obesity-related conditions, especially Type 2 Diabetes.
- Those who have struggled with severe acid reflux.
- Patients who have not achieved their goals with a previous gastric sleeve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gastric sleeve and gastric bypass are two effective weight loss options for individuals with obesity. The decision of which procedure to have should be made with the guidance of a qualified bariatric surgeon and should take into consideration individual health status, weight history, and personal preferences. Patients who undergo bariatric surgery should also be prepared for lifestyle changes to achieve long-term weight loss success.
Choosing the right procedure and committing to the necessary lifestyle changes can lead to significant health improvements and a better quality of life for individuals struggling with obesity.